THE INTRODUCTION OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Before we talk about the health science side of this topic, let us first understand the theory of respiratory system.
Respiration is the process of exchanging gas between the atmosphere and the body cells.
Before we talk about the health science side of this topic, let us first understand the theory of respiratory system.
Respiration is the process of exchanging gas between the atmosphere and the body cells.

The NASAL CAVITY (nose) is the preferred entrance for outside air into the Respiratory System. The hairs that line the inside wall are part of the air-cleansing system.
Air also enters through the ORAL CAVITY (mouth), especially in people who have a mouth-breathing habit or whose nasal passages may be temporarily obstructed, as by a cold.
The PHARYNX (throat) collects incoming air from the nose and passes it downward to the trachea (windpipe).
The LARYNX (voice box) contains the vocal cords. It is the place where moving air being breathed in and out creates voice sounds.
The TRACHEA (windpipe) is the passage leading from the pharynx to the lungs.
The trachea divides into the two main BRONCHI (tubes), one for each lung. These, in turn, subdivide further into bronchioles.
Air also enters through the ORAL CAVITY (mouth), especially in people who have a mouth-breathing habit or whose nasal passages may be temporarily obstructed, as by a cold.
The PHARYNX (throat) collects incoming air from the nose and passes it downward to the trachea (windpipe).
The LARYNX (voice box) contains the vocal cords. It is the place where moving air being breathed in and out creates voice sounds.
The TRACHEA (windpipe) is the passage leading from the pharynx to the lungs.
The trachea divides into the two main BRONCHI (tubes), one for each lung. These, in turn, subdivide further into bronchioles.
Additional: this video shows you someone's trachea using a camera:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sU_8juD3YzQ
The bronchial tubes are lined with CILIA (like very small hairs) that have a wave-like motion. This motion carries MUCUS (sticky phlegm or liquid) upward and out into the throat, where it is either coughed up or swallowed. The mucus catches and holds much of the dust, germs, and other unwanted matter that has invaded the lungs and thus gets rid of it.
The smallest subdivisions of the bronchi are called BRONCHIOLES, at the ends of which are the alveoli (plural of alveolus).
The ALVEOLI are the very small air sacs that are the destination of air breathed in. The CAPILLARIES are blood vessels that are imbedded in the walls of the alveoli. Blood passes through the capillaries, brought to them by the PULMONARY ARTERY and taken away by the PULMONARY VEIN. While in the capillaries the blood discharges carbon dioxide into the alveoli and takes up oxygen from the air in the alveoli.
The bronchial tubes are lined with CILIA (like very small hairs) that have a wave-like motion. This motion carries MUCUS (sticky phlegm or liquid) upward and out into the throat, where it is either coughed up or swallowed. The mucus catches and holds much of the dust, germs, and other unwanted matter that has invaded the lungs and thus gets rid of it.
The smallest subdivisions of the bronchi are called BRONCHIOLES, at the ends of which are the alveoli (plural of alveolus).
The ALVEOLI are the very small air sacs that are the destination of air breathed in. The CAPILLARIES are blood vessels that are imbedded in the walls of the alveoli. Blood passes through the capillaries, brought to them by the PULMONARY ARTERY and taken away by the PULMONARY VEIN. While in the capillaries the blood discharges carbon dioxide into the alveoli and takes up oxygen from the air in the alveoli.
MECHANISM OF BREATHING
Respiration requires inhaling and exhaling, or breathing. Breathing is the process by which oxygen in the air is brought into the lungs and into close contact with the blood, which absorbs it and carries it to all parts of the body. At the same time the blood gives up waste matter (carbon dioxide), which is carried out of the lungs with the air breathed out.
When you breathe properly (that is with the mouth closed so that the air is inhaled through nasal passages) oxygen travels down the pharynx (rear of the throat), the larynx (roughly in the area of Adam's apple), and the trachea or windpipe until it reaches the bronchial tubes. By then most of the dust and bacteria have been filtered out by the mucous membranes, or the moist lining of the nose. Mucous, by the way, in addition to acting as filter substances, also has certain germicidal properties-another reason why it is so important to cultivate the habit of breathing though the nose. A third reason is that while traveling this somewhat longer road the air is warmed to proper body temperature, which means extra insurance against catching colds.
After having thus filtered and warmed, the supply of air moves on from the bronchiole into the lungs. Here it enters millions of cells-600, 000,000 of them to be exact, if you can visualize such an astronomic figure-each of which is a tiny air sac. Surrounding these is a network of equally tiny blood vessels or capillaries. The blood absorbs the fresh oxygen directly through the cell walls at the same time as it rids itself of the carbon dioxide from the last trip.
Next the freshly oxygenated blood travels to the heart. The heart pumps it via arteries and blood vessels to every part of the body, where in turn it seeps into every tissue and bone cell. In this manner 800 quarts of blood pass through the heart and lungs every hour. Small wonder, then that the condition of your heart so closely governs you life expectancy!
To understand the mechanism of breathing, please take a look at this video:
Once the air reaches the alveoli, gas exchange process occurs. Take a look at this video to see further about the gas exchange:
Respiration requires inhaling and exhaling, or breathing. Breathing is the process by which oxygen in the air is brought into the lungs and into close contact with the blood, which absorbs it and carries it to all parts of the body. At the same time the blood gives up waste matter (carbon dioxide), which is carried out of the lungs with the air breathed out.
When you breathe properly (that is with the mouth closed so that the air is inhaled through nasal passages) oxygen travels down the pharynx (rear of the throat), the larynx (roughly in the area of Adam's apple), and the trachea or windpipe until it reaches the bronchial tubes. By then most of the dust and bacteria have been filtered out by the mucous membranes, or the moist lining of the nose. Mucous, by the way, in addition to acting as filter substances, also has certain germicidal properties-another reason why it is so important to cultivate the habit of breathing though the nose. A third reason is that while traveling this somewhat longer road the air is warmed to proper body temperature, which means extra insurance against catching colds.
After having thus filtered and warmed, the supply of air moves on from the bronchiole into the lungs. Here it enters millions of cells-600, 000,000 of them to be exact, if you can visualize such an astronomic figure-each of which is a tiny air sac. Surrounding these is a network of equally tiny blood vessels or capillaries. The blood absorbs the fresh oxygen directly through the cell walls at the same time as it rids itself of the carbon dioxide from the last trip.
Next the freshly oxygenated blood travels to the heart. The heart pumps it via arteries and blood vessels to every part of the body, where in turn it seeps into every tissue and bone cell. In this manner 800 quarts of blood pass through the heart and lungs every hour. Small wonder, then that the condition of your heart so closely governs you life expectancy!
To understand the mechanism of breathing, please take a look at this video:
Once the air reaches the alveoli, gas exchange process occurs. Take a look at this video to see further about the gas exchange:
For your further information, this website link can give you more information about the respiratory system:
And from this link, you can learn also about the respiratory system in a more fun way with the fun facts in it:
- By: Jessica Giovanni -
After understanding the theories of respiratory system, let us now talk about..........
THE DISORDERS OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The first one is ASTHMA. Asthma is caused by the constriction or the narrowing of the bronchioles by the muscles in their walls. This makes a difficulty for the air to get in and out of the lungs and medicines to reduce the constriction.
What to do during the attack?
1. sit leaning forward or in a semi-prone position to help restore normal breathing.
2. Try placing a hot, moist towel over your chest to help relax your chest muscles and restore normal breathing.
How to prevent another attack?
1. Incorporate breathing exercises into daily routine to help strengthen the respiratory muscles.
2. Keep a healthy diary.
3. Avoid perfumes.
4. Make a special effort to keep the environment allergen free.
5. Get an air purifier. Dust and vacuum often. Change the home furnace or air conditioner filter regular.
6. Stop exercising if start wheezing or feel an attack coming on.
7. Drink plenty of water
8. DO NOT smoke!
Addition: many people who have an asthma say that swimming regularly is a good way of reducing the chance of asthma attacks.
The second one is BRONCHITIS. Bronchitis is caused by inflammation of the lining of the bronchioles, may be due to infection from bacteria, viruses, or chemicals such as those contained in the tobacco smoke.
how to prevent bronchitis: DO NOT smoke! and drink A LOT of water.
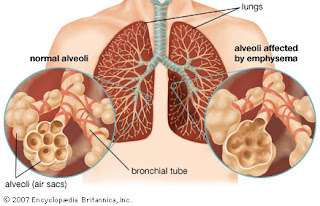
The third one is EMPHYSEMA. Emphysema is a condition in which the structure of the alveoli is broken down, reducing the surface area for gaseous exchange, as well as damaging the elasticity of the lungs.
How to prevent emphysema?
1. avoid air pollution.
2. DO NOT smoke!
The fourth one is LUNG CANCER. Lung cancer is caused by the unusual division of cells inside the lungs (out of control), and could disturb the normal function of lungs. Natural gas such as the radon gas could cause lung cancer. But the main cause of this disease is smoking. It is hard to find early and difficult to treat. It is one of the more miserable cancers to suffer from. However, lung cancer is also one of the most preventable types of cancer. By avoiding certain risk factors for lung cancer, we can reduce the chances of developing it.
How to prevent lung cancer:
1. Stop smoking NOW! - if you are a smoker.
2. Keep away from secondhand smoke.

This video can explain to you the symptoms of emphysema and lung cancer:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kBPQYUUiZm8
For additional information, you can see this video to find another respiratory disorder:
For additional information, you can see this video to find another respiratory disorder:
So from the discussion above, we can conclude that most of the respiratory disorders are caused by SMOKING.
This video can explain more to you how smoking affects your respiratory system:
Are you a smoker? And you are afraid of the smoking effects? You want to quit smoking but you found it is very difficult? Please take a look at this video:
For further information about respiratory disorders, you can go to this links:
- By: Jessica Giovanni -